Diagonal Oblong Chess
Some chess variant inventors have done efforts modifying F.I.D.E. chess to make Bishop more powerful. One of the methods is to modify the shape of board and setup. King Arthur's Chess 72 has a round or cylinder board with an odd number of files which unbind Bishop with colors. Balbo's chess, Longshanks Chess, and Troitzky Chess (their objects may not be to strengthen Bishop) have similar methods that rotate the board by 45 degree to make a diagonal square board. But players are playing corner to corner. Every pawn has a different distance to promote. The setups are very different from F.I.D.E. chess, and castling doesn’t exist. Left and Right corners that Pawns can not cover become very important. There may be other variants that I haven't noticed. Diagonal Oblong Chess invented by Shi Ji is another experiment by modifying the shape of board. A similar board with different size was used in UOS and Oblique. There are 64 cells as F.I.D.E. chess, but arranged very differently. Players are playing side to side. The setup is similar to that of F.I.D.E. chess. Pawn rules are similar to those of Diagonal Chess and Double Diamond. Pawns can promote by moving by an equal distance and they can cover every file. Bishop becomes colorbound Rook, and Rook becomes colorfree Bishop. There are also castling & guarding rules, but slightly different from that of F.I.D.E. chess.Setup
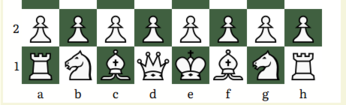
\a /\c /\e /\g /\ 1\/r \/k \/n \/b \ 6/\ /\ /\ /\ / /b \/n \/q \/r \/1 \ /\ /\ /\ /\5 1\/p \/p \/p \/p \ 4/\ /\ /\ /\ / /p \/p \/p \/p \/1 \ /\ /\ /\ /\3 1\/ \/ \/ \/ \ 2/\ /\ /\ /\ / / \/ \/ \/ \/1 \ /\ /\ /\ /\1 1\/ \/ \/ \/ \ 0/\ /\ /\ /\ / / \/ \/ \/ \/9 \ /\ /\ /\ /\ 8\/ \/ \/ \/ \ /\ /\ /\ /\ / / \/ \/ \/ \/7 \ /\ /\ /\ /\ 6\/ \/ \/ \/ \ /\ /\ /\ /\ / / \/ \/ \/ \/5 \ /\ /\ /\ /\ 4\/P \/P \/P \/P \ /\ /\ /\ /\ / /P \/P \/P \/P \/3 \ /\ /\ /\ /\ 2\/R \/Q \/N \/B \ /\ /\ /\ /\ / /B \/N \/K \/R \/1 \ /\ /\ /\ /\ \/b \/d \/f \/h \The cells are differently numbered from F.I.D.E. chess board. Files and ranks go diagonally. Files of a c e and g have only odd numbered ranks as 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 and 15, whereas files of b d f and h have only even numbered ranks as 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 and 16.
Pieces
Rook Bishop and Knight are the same as F.I.D.E. chess. King and Queen move same as F.I.D.E. chess but have different Castling & Guarding rules. Pawn’s rules are modified to fit new board.Pawn
Pawns move diagonally forward and capture orthogonally forward. Pawns on starting positions can move one or two squares diagonally forward. They can be captured en passant advancing two squares. Pawns can promote to any major pieces except the King on last ranks of every 8 files (the starting positions of the opponents’ major pieces).Rules
Rules are the same to F.I.D.E. chess, except Pawns' move (see Pieces --> Pawn), castling rules and guarding rules.Castling
King can castle only with the left bishop (Ba1 for white, black Bh16), as long as they are never moved, a1 c1 and e1 are not under attack and c1 is empty. King moves to a1 and the Bishop moves to c1 (for white, black symmetric).Guarding
Queen can guard only with the right Bishop (Bh2 for white, black Ba15), as long as they are never moved, and f2 is empty. When guarding, wherever Queen moves, the Bishop moves to d2. Queen can even move to f2 and h2 where the right Bishop stayed (for white, black symmetric). Queen can chose to make a single move without guarding. This 'user submitted' page is a collaboration between the posting user and the Chess Variant Pages. Registered contributors to the Chess Variant Pages have the ability to post their own works, subject to review and editing by the Chess Variant Pages Editorial Staff.
This 'user submitted' page is a collaboration between the posting user and the Chess Variant Pages. Registered contributors to the Chess Variant Pages have the ability to post their own works, subject to review and editing by the Chess Variant Pages Editorial Staff.
By Shi Ji.
Web page created: 2010-12-05. Web page last updated: 2010-12-14